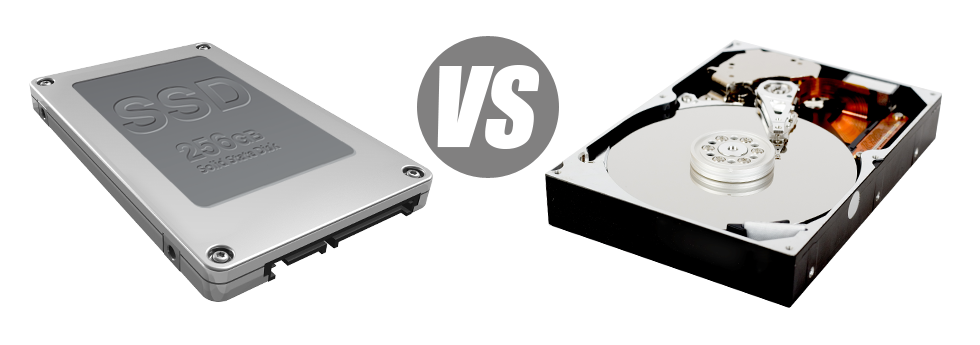
For years there was only one reputable way for you to store data on a computer – utilizing a hard drive (HDD). Having said that, this sort of technology is presently demonstrating it’s age – hard disks are loud and slow; they can be power–hungry and have a tendency to generate a great deal of heat for the duration of intense operations.
SSD drives, in contrast, are swift, take in significantly less energy and are far less hot. They offer a new approach to file accessibility and data storage and are years ahead of HDDs when considering file read/write speed, I/O performance and energy effectivity. Discover how HDDs stand up against the newer SSD drives.
1. Access Time
With the release of SSD drives, file accessibility rates have gone through the roof. With thanks to the unique electronic interfaces made use of in SSD drives, the average file access time has been reduced towards a record low of 0.1millisecond.
The technology behind HDD drives dates all the way to 1954. And while it’s been considerably enhanced throughout the years, it’s still can’t stand up to the imaginative technology powering SSD drives. Utilizing today’s HDD drives, the very best file access speed you’ll be able to achieve can vary somewhere between 5 and 8 milliseconds.
2. Random I/O Performance
The random I/O performance is important for the operation of any data file storage device. We’ve executed extensive trials and have established that an SSD can deal with at the least 6000 IO’s per second.
All through the same trials, the HDD drives proved to be significantly slower, with 400 IO operations handled per second. Although this seems to be a significant number, when you have an overloaded web server that serves loads of well known websites, a sluggish hard disk drive can cause slow–loading web sites.
3. Reliability
SSD drives are meant to have as less moving elements as is possible. They use a comparable concept like the one utilized in flash drives and are significantly more trustworthy rather than common HDD drives.
SSDs have an common failure rate of 0.5%.
As we have already noted, HDD drives rely on spinning disks. And something that employs numerous moving elements for prolonged intervals is susceptible to failing.
HDD drives’ average rate of failure can vary among 2% and 5%.
4. Energy Conservation
SSDs don’t have moving elements and require hardly any cooling energy. In addition, they demand very little electricity to work – trials have demonstrated they can be operated by a common AA battery.
As a whole, SSDs take in between 2 and 5 watts.
From the minute they have been created, HDDs have invariably been very energy–hungry devices. So when you have a web server with many different HDD drives, this will certainly boost the regular utility bill.
Normally, HDDs take in somewhere between 6 and 15 watts.
5. CPU Power
Because of SSD drives’ greater I/O performance, the main server CPU can work with file queries a lot quicker and save time for different operations.
The normal I/O delay for SSD drives is 1%.
When using an HDD, you need to dedicate extra time waiting around for the outcome of your data file ask. It means that the CPU will remain idle for further time, expecting the HDD to reply.
The standard I/O delay for HDD drives is approximately 7%.
6.Input/Output Request Times
Almost all of SuntechSpace’s new machines now use exclusively SSD drives. Our personal tests have demostrated that by using an SSD, the typical service time for any I/O request whilst doing a backup remains under 20 ms.
During the same trials using the same server, now equipped out with HDDs, overall performance was considerably sluggish. All through the web server data backup process, the standard service time for I/O calls fluctuated somewhere between 400 and 500 ms.
7. Backup Rates
You’re able to check out the real–world potential benefits to using SSD drives on a regular basis. By way of example, with a web server designed with SSD drives, a full data backup can take only 6 hours.
Over time, we’ve worked with mainly HDD drives with our servers and we’re familiar with their functionality. On a hosting server designed with HDD drives, an entire server back up may take about 20 to 24 hours.
Should you want to instantaneously add to the effectiveness of your respective web sites with no need to modify any kind of code, an SSD–equipped web hosting service will be a very good alternative. Examine the Linux website hosting packages and the Linux VPS web hosting – these hosting services feature extremely fast SSD drives and are available at affordable prices.
Hepsia
- Live Demo
Service guarantees
- Register now. There aren’t any installation fees and you will have total root access to your server. 99.9% network uptime is guaranteed.
Compare our prices
- Effortlessly examine the parameters and tools provided by SuntechSpace’s Virtual Private Servers. Find which VPS Web Hosting configuration will provide you with precisely what you need to take care of your dynamic web presence with no trouble.
- Compare our hosting plans
Contact Us
- It is easy to make contact with us around the clock by email or by making use of our extra–fast ticketing platform. Our company offers a 1–hour reply time guarantee.